In the modern economic landscape, grasping the concept of interest rates is more important than ever. Whether you're a homeowner, an investor, or someone managing personal finances, interest rates significantly influence your financial choices. From borrowing money to saving and investing, these rates shape the financial environment. As we explore this topic, we will uncover the intricacies of interest rates and their implications for individuals and businesses alike.
Interest rates today reflect broader economic conditions and are shaped by central banks, inflation rates, and global market trends. By understanding these dynamics, individuals can make smarter decisions regarding loans, savings, and investments. This article provides an in-depth look at interest rates, their determinants, and their effects on various aspects of personal and corporate finance.
As we journey through this guide, we will examine the historical context of interest rates, the factors that influence them, and practical strategies to manage financial risks associated with fluctuating rates. Whether you're an experienced investor or new to the world of finance, this article will equip you with the knowledge needed to succeed in today's financial environment.
Read also:Exploring The Cia Headquarters A Pillar Of Global Intelligence
Table of Contents
- Understanding Today's Interest Rates
- What Exactly Are Interest Rates?
- Key Factors Influencing Interest Rates
- The Role of Central Banks in Shaping Interest Rates
- How Inflation Affects Interest Rates
- The Relationship Between Interest Rates and the Economy
- Interest Rates and Loan Products
- Savings Accounts in a Changing Interest Rate Environment
- Investing Successfully Amid Fluctuating Interest Rates
- Global Trends Shaping Today's Interest Rates
- Conclusion and Practical Insights
Understanding Today's Interest Rates
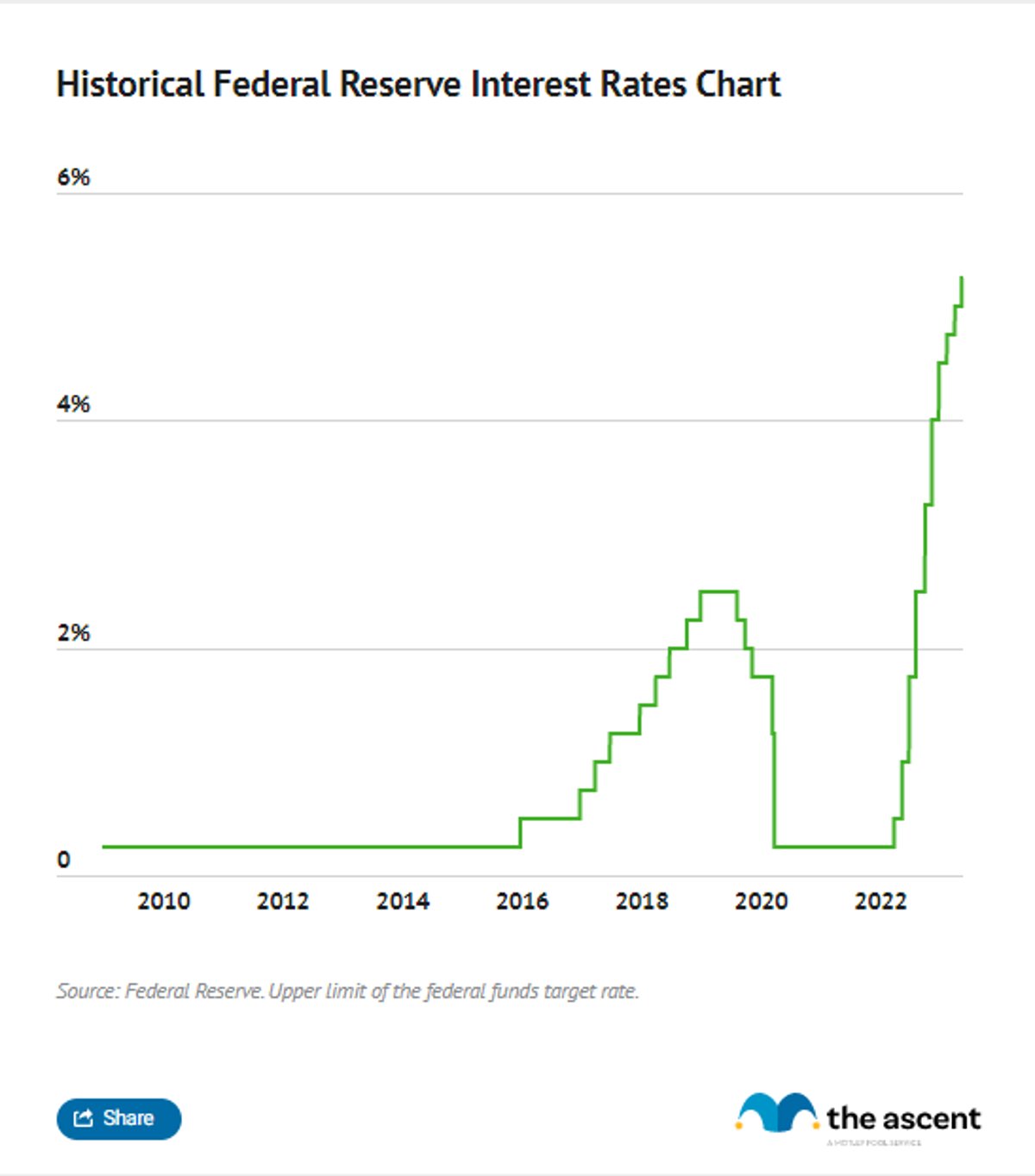
Interest rates today serve as a cornerstone of the financial system, acting as a gauge for economic health and stability. When central banks adjust interest rates, they aim to control inflation, stimulate growth, or stabilize currency values. Grasping these rates is essential for anyone seeking to manage their finances effectively.
Historically, interest rates have varied due to factors such as economic cycles, geopolitical events, and technological advancements. In recent years, the global financial crisis and subsequent recovery efforts have significantly impacted interest rates. This section will provide a comprehensive overview of how these rates have evolved and their current state in the global market.
What Exactly Are Interest Rates?
Interest rates represent the cost of borrowing money, expressed as a percentage of the principal amount. They serve as compensation for lenders, accounting for the risk of lending and the opportunity cost of not using the funds elsewhere. In essence, interest rates function as a mechanism to balance the supply and demand for capital.
Types of Interest Rates
- Fixed Interest Rates: Remain constant throughout the loan term, offering predictability and stability.
- Variable Interest Rates: Fluctuate based on market conditions, providing flexibility but introducing potential risks.
- Prime Interest Rates: The lowest rate offered by banks to their most creditworthy customers, serving as a benchmark for other rates.
Understanding the different types of interest rates is crucial for making informed financial decisions. Each type carries its own advantages and risks, which we will explore further in subsequent sections.
Key Factors Influencing Interest Rates
Several factors contribute to the determination of interest rates, including economic growth, inflation rates, monetary policy, and global market conditions. Central banks play a critical role in setting benchmark rates, which influence consumer and business lending rates.
Primary Drivers of Interest Rates
- Economic Growth: Stronger economies often lead to higher interest rates as borrowing increases.
- Inflation: Central banks adjust rates to control inflation levels, ensuring price stability.
- Monetary Policy: Decisions by central banks directly impact interest rates, aligning them with broader economic goals.
The Federal Reserve emphasizes inflation targeting as a key strategy in setting interest rates. This approach ensures price stability and supports sustainable economic growth. By monitoring these factors, individuals and businesses can better anticipate changes in interest rates.
Read also:Tre Jones A Rising Star In Basketball
The Role of Central Banks in Shaping Interest Rates
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States and the European Central Bank, are responsible for setting benchmark interest rates. These institutions use monetary policy tools to influence economic activity and maintain financial stability. For instance, during economic downturns, central banks may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing and spending.
Data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) highlights the significance of central bank independence in managing interest rates. By remaining neutral, central banks can make data-driven decisions rather than succumbing to political pressures. This ensures that interest rates remain aligned with broader economic objectives.
How Inflation Affects Interest Rates
Inflation is a primary determinant of interest rates. When inflation rises, the purchasing power of money decreases, prompting central banks to raise interest rates to curb excessive spending. Conversely, during periods of low inflation or deflation, central banks may lower rates to stimulate economic activity.
A report by the World Bank indicates that inflation targeting has become a widely adopted strategy among central banks. This approach involves setting a target inflation rate and adjusting interest rates accordingly. By maintaining a stable inflation rate, central banks can promote economic growth and financial stability.
The Relationship Between Interest Rates and the Economy
Interest rates have a profound impact on the economy, influencing consumer behavior, business investment, and government spending. For example, lower interest rates can encourage borrowing and spending, boosting economic growth. Conversely, higher rates may discourage borrowing and slow economic activity.
Key Economic Indicators to Monitor
- GDP Growth Rate: Reflects the overall health of the economy, providing insights into its expansion or contraction.
- Unemployment Rate: Indicates labor market conditions, signaling the availability of jobs and economic stability.
- Consumer Confidence Index: Measures consumer sentiment and spending behavior, offering a glimpse into future economic trends.
By tracking these economic indicators, individuals and businesses can gain valuable insights into the direction of interest rates. This knowledge enables them to make informed decisions about loans, savings, and investments.
Interest Rates and Loan Products
Interest rates directly affect the cost of borrowing for various loan products, including mortgages, auto loans, and personal loans. Lenders use benchmark rates set by central banks to determine the interest rates they offer to consumers. Consequently, changes in benchmark rates can significantly impact monthly payments and overall borrowing costs.
Popular Loan Products
- Mortgage Loans: Long-term loans used to purchase real estate, often with fixed or variable rates.
- Auto Loans: Loans specifically designed for purchasing vehicles, offering competitive rates and terms.
- Personal Loans: Unsecured loans for various personal expenses, providing flexibility and convenience.
A study by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) reveals that even minor changes in interest rates can result in substantial savings or additional costs for borrowers. By understanding the relationship between interest rates and loan products, consumers can make more cost-effective borrowing decisions.
Savings Accounts in a Changing Interest Rate Environment
Savings accounts are a popular way to store and grow money over time. The interest earned on these accounts is directly tied to prevailing interest rates. When rates are high, savers benefit from higher returns on their deposits. Conversely, during periods of low rates, savings account yields may be minimal.
Financial institutions such as banks and credit unions offer various types of savings accounts, each with distinct interest rate structures. For example, high-yield savings accounts typically offer competitive rates but may require higher minimum balances. By comparing interest rates and account features, savers can maximize their returns and achieve their financial goals.
Investing Successfully Amid Fluctuating Interest Rates
Investors must consider the impact of fluctuating interest rates on their portfolios. Rising rates can lead to lower bond prices, while falling rates may result in higher prices. Additionally, interest rates can influence stock market performance by affecting corporate borrowing costs and consumer spending.
Strategies for Managing Investment Risk
- Diversification: Spreading investments across asset classes to reduce risk and enhance potential returns.
- Duration Management: Adjusting bond portfolios to align with interest rate expectations, optimizing performance.
- Hedging: Utilizing derivatives to protect against adverse rate movements, safeguarding investment value.
Investors should regularly review their portfolios and adapt strategies to changing interest rate environments. By staying informed about economic trends and central bank decisions, investors can make more strategic investment choices and achieve long-term success.
Global Trends Shaping Today's Interest Rates
Interest rates today are influenced by global economic trends and geopolitical events. For instance, ongoing trade tensions between major economies have introduced uncertainty into financial markets, prompting central banks to adopt accommodative monetary policies. Additionally, the growing emphasis on climate change and sustainable finance initiatives is reshaping the future of interest rates worldwide.
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) predicts that global interest rates will remain low in the near term as central banks focus on supporting economic recovery. However, as economic conditions improve, gradual rate increases may occur to ensure long-term stability and sustainable growth.
Conclusion and Practical Insights
Interest rates today play a pivotal role in shaping the financial landscape. They influence borrowing costs, impact investment returns, and affect economic stability. Understanding these rates is essential for making informed financial decisions. By monitoring economic indicators, staying informed about central bank policies, and adapting strategies to changing conditions, individuals and businesses can navigate the complexities of interest rates effectively.
We encourage readers to take action by reviewing their financial plans and adjusting strategies as needed. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below, and explore other articles on our site for additional insights into personal finance and investing. Together, we can build a more financially secure future.