The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) plays a vital role in shaping the economic landscape of the United States. As the primary monetary policymaking body of the Federal Reserve System, the FOMC's decisions influence interest rates, inflation, and employment rates across the country. Gaining insight into its functions and responsibilities is essential for anyone interested in macroeconomics, finance, or investment.
The FOMC is far more than just an acronym in the financial world; it serves as the backbone of U.S. monetary policy. Its meetings and announcements are closely monitored by economists, investors, and businesses because they set the tone for economic activities. Whether you're an experienced investor or a curious beginner, understanding the workings of the FOMC can provide profound insights into the health and trajectory of the economy.
This article will explore the complexities of the FOMC, from its history and structure to its decision-making processes and global influence. By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of how the FOMC operates and why its actions matter to you. Let's dive in.
Read also:The Intense Rivalry Between Denver Nuggets And Los Angeles Lakers
Table of Contents
- Introduction to FOMC
- History of FOMC
- Structure of FOMC
- FOMC Meetings
- Monetary Policy Tools
- Impact on the Economy
- Global Influence of FOMC
- Challenges Facing the FOMC
- Future of FOMC
- Conclusion
Introduction to FOMC
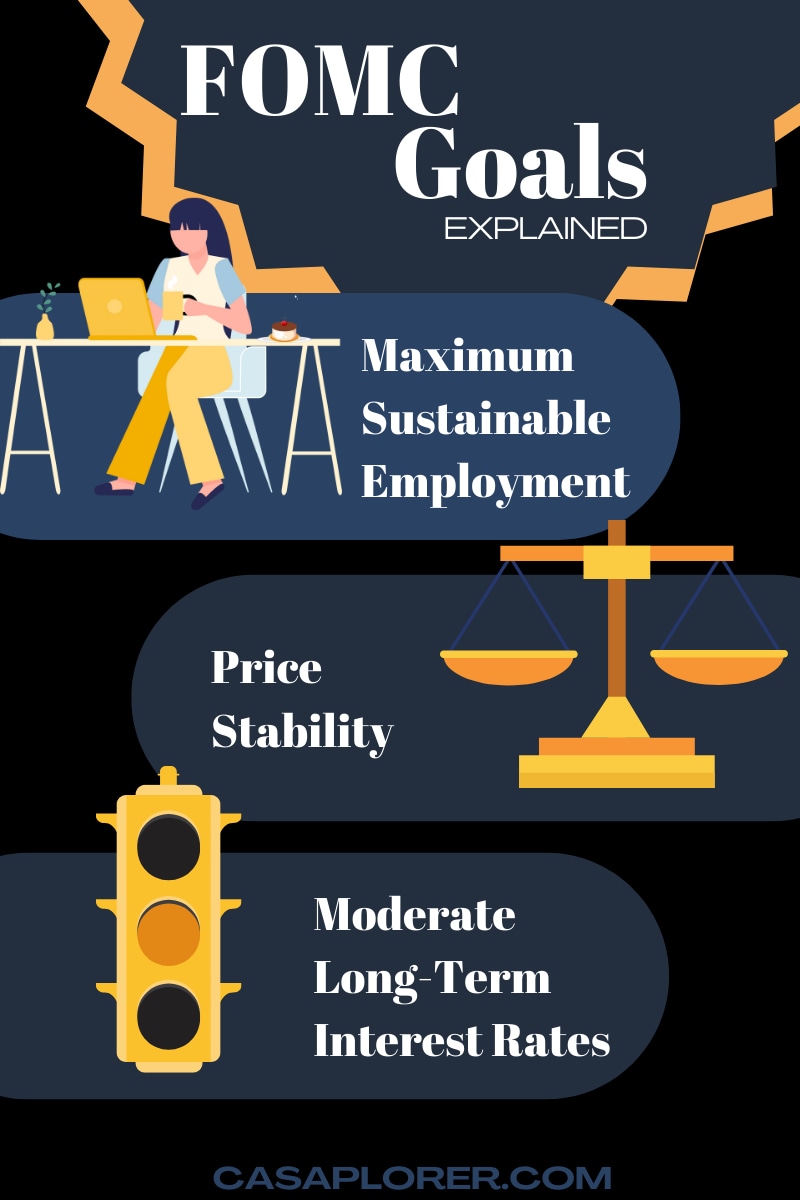
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) is a fundamental component of the Federal Reserve System, tasked with implementing monetary policy in the United States. Established in 1913 under the Federal Reserve Act, the FOMC's primary mission is to promote maximum employment, ensure price stability, and maintain moderate long-term interest rates.
FOMC's Role in the Economy
The FOMC plays a dual role in the U.S. economy: it conducts open market operations and determines the federal funds rate. These actions influence the cost of borrowing, consumer spending, and overall economic activity. By skillfully adjusting these tools, the FOMC strives to achieve its dual mandate of employment and price stability. Its decisions have a profound impact on the financial well-being of individuals, businesses, and the nation as a whole.
Why the FOMC Matters to You
The decisions made by the FOMC have far-reaching consequences. For instance, changes in interest rates can affect mortgage rates, credit card rates, and even stock market performance. Understanding the FOMC's role empowers individuals and businesses to make informed financial decisions, helping them navigate the complexities of the modern economy.
History of FOMC
The FOMC was officially established in 1935 as part of the Banking Act. Initially, its responsibilities were limited, but over the decades, its role has expanded significantly. The Great Depression and subsequent economic challenges underscored the need for a more proactive monetary policy-making body, leading to the FOMC's evolution into the powerful entity it is today.
Key Milestones in the Evolution of FOMC
From its modest beginnings, the FOMC has undergone significant transformations. Notable milestones include the introduction of quantitative easing during the 2008 financial crisis and the adoption of forward guidance as a policy tool. These developments have enhanced the FOMC's ability to address complex economic challenges and foster economic stability.
Structure of FOMC
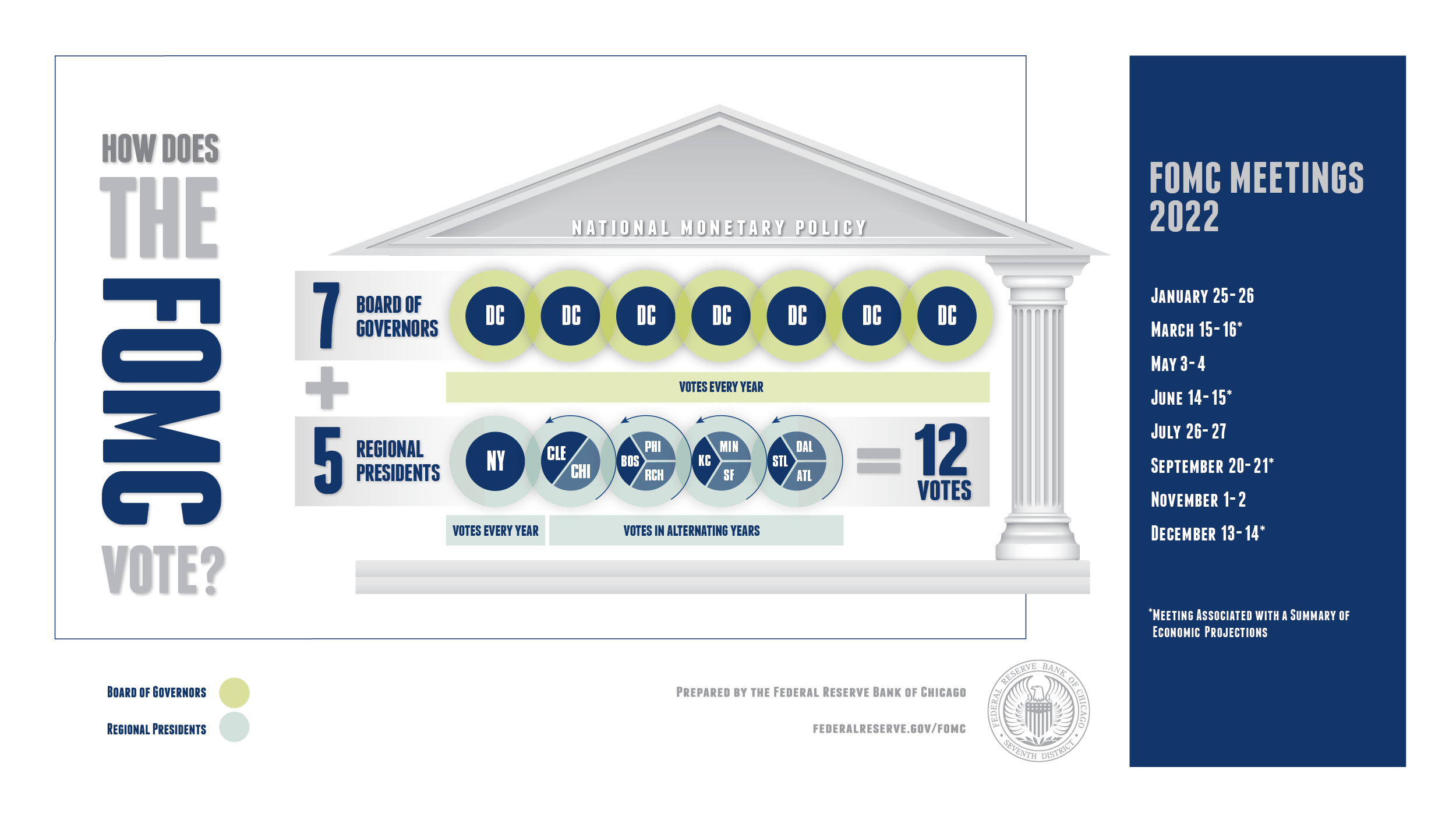
The FOMC is composed of twelve members: seven members of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System and five of the eleven Reserve Bank presidents. The Federal Reserve Bank of New York always has a seat on the committee, while the remaining four seats rotate among the other Reserve Banks. This structure ensures diverse perspectives and regional representation in decision-making.
Read also:Rondale Moore The Rising Star Redefining The Nfl Wide Receiver Role
Key Members and Their Roles
- Chair of the Federal Reserve: Leads the FOMC and plays a central role in shaping monetary policy decisions.
- Board of Governors: Provides strategic direction and oversight, ensuring the FOMC operates in alignment with broader economic goals.
- Reserve Bank Presidents: Contribute regional perspectives and expertise, enriching the decision-making process with insights from various parts of the country.
FOMC Meetings
The FOMC holds eight regularly scheduled meetings each year, with additional meetings convened as needed. During these meetings, members thoroughly review economic and financial conditions, determine monetary policy, and assess risks to the outlook. The meetings are structured to ensure comprehensive analysis and thoughtful decision-making.
Meeting Agenda and Process
- Economic Data Analysis: A detailed review of GDP growth, inflation rates, and employment figures to gauge the health of the economy.
- Monetary Policy Decisions: Adjustments to the federal funds rate and other policy tools to align with economic objectives.
- Press Conference: Public communication of decisions and the economic outlook, fostering transparency and accountability.
Monetary Policy Tools
The FOMC employs a variety of tools to influence the economy, including open market operations, reserve requirements, and the discount rate. These tools help regulate the money supply and credit conditions, ensuring the economy operates within desired parameters.
Quantitative Easing: A Key Policy Tool
Quantitative easing (QE) involves the purchase of government securities to increase the money supply and encourage lending and investment. This tool was extensively utilized during the 2008 financial crisis and subsequent recovery, playing a crucial role in stabilizing the economy and fostering growth.
Impact on the Economy
The FOMC's decisions have a direct and significant impact on various economic indicators. For example, lower interest rates can stimulate borrowing and spending, driving economic growth. Conversely, higher rates can curb inflation but may slow economic activity, highlighting the delicate balance the FOMC must maintain.
Inflation Targeting: A Cornerstone of FOMC Policy
Inflation targeting is a cornerstone of the FOMC's mandate. By adjusting interest rates, the committee aims to keep inflation within a target range, typically around 2%. This helps preserve purchasing power, maintain economic stability, and ensure long-term prosperity for the nation.
Global Influence of FOMC
The FOMC's actions have global implications, affecting international trade, exchange rates, and capital flows. Changes in U.S. interest rates can lead to shifts in global investment patterns and currency valuations, demonstrating the interconnectedness of the global economy.
Impact on Emerging Markets
Emerging markets are particularly sensitive to FOMC decisions. Higher U.S. interest rates can attract capital inflows, leading to currency appreciation and increased borrowing costs for these countries. This highlights the importance of the FOMC's role in maintaining global economic stability and fostering sustainable growth.
Challenges Facing the FOMC
Despite its influence, the FOMC faces numerous challenges, including political pressures, economic uncertainties, and global events. Balancing its dual mandate while navigating these challenges requires careful consideration, strategic planning, and a commitment to transparency and accountability.
Navigating Political Pressures
The FOMC operates independently but is not immune to political influences. Policymakers often face scrutiny and criticism from government officials and the public, making it essential to maintain transparency and accountability. By fostering open communication and engaging with stakeholders, the FOMC can build trust and enhance its effectiveness.
Future of FOMC
As the global economy continues to evolve, the FOMC must adapt to new challenges and opportunities. Emerging technologies, climate change, and demographic shifts will likely shape the committee's approach to monetary policy in the coming years, requiring innovation and flexibility.
Exploring Innovative Policy Tools
The FOMC may explore innovative policy tools, such as digital currencies and climate-focused monetary policies, to address the evolving needs of the economy. These tools could enhance the effectiveness and reach of monetary policy, ensuring the FOMC remains at the forefront of economic policymaking.
Conclusion
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) is a cornerstone of U.S. monetary policy, influencing economic conditions both domestically and globally. Understanding its functions, structure, and decision-making processes is essential for anyone interested in finance and economics. By staying informed about the FOMC's activities and decisions, individuals and businesses can better navigate the complexities of the modern economy.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and insights in the comments section below. Additionally, explore other articles on our site to deepen your understanding of financial topics. Together, let's continue learning and growing in the ever-changing world of finance.